Experts Warn Lithium Mining Might Destroy Fragile Ecosystem
According to sources, between 2015 to 2018, the demand for lithium carbonate a key ingredient in manufacturing rechargeable batteries tripled.
Despite the uncertainties of the previous year, there is a potential or existing demand for tech products like electric vehicles (EVs), smartphones which would cause a more balanced lithium market expected in 2021.
Experts claim that Lithium carbonate demand is expected to increase by 23 percent in 2021.
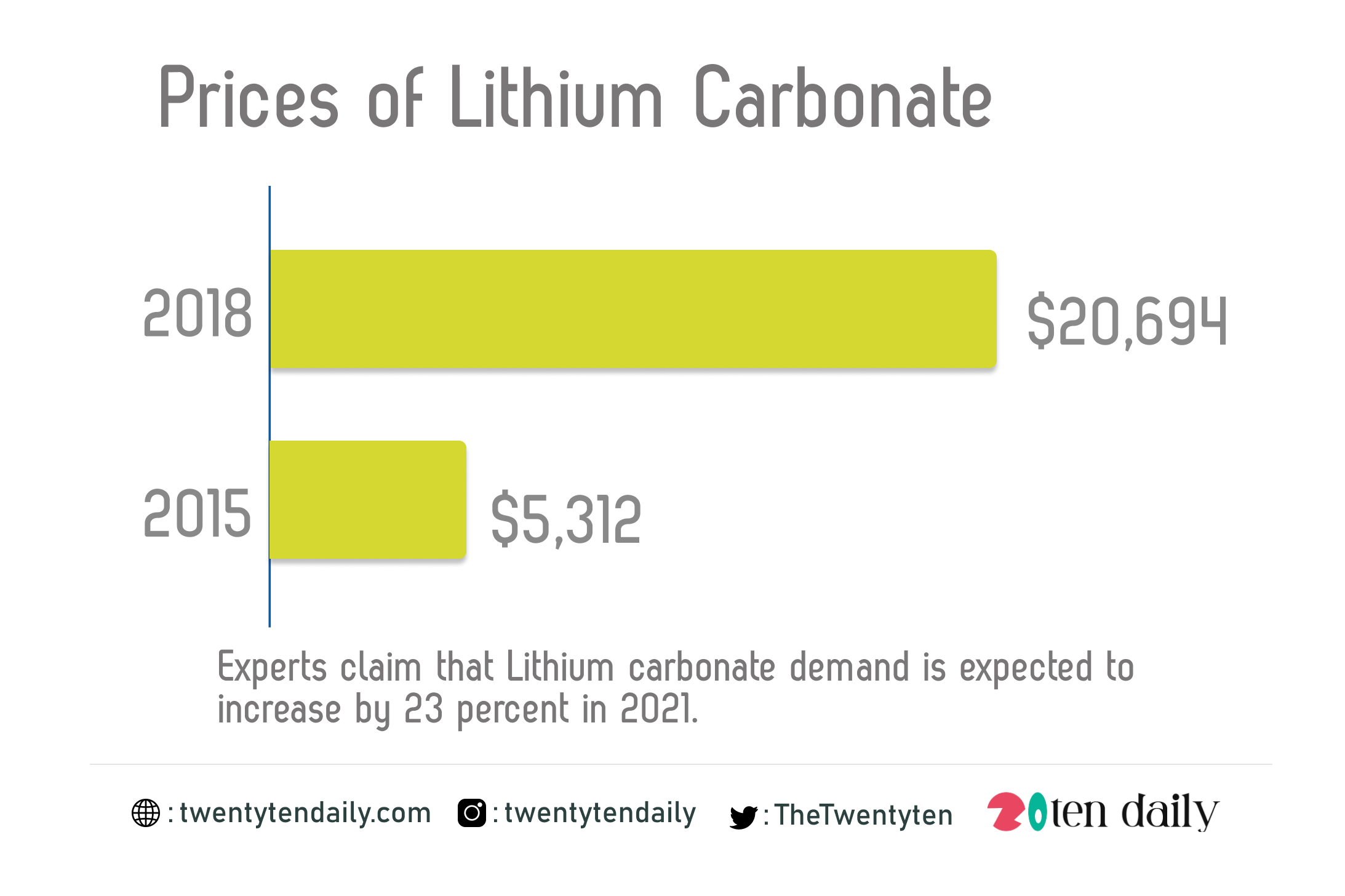
For instance, the demand from electric car makers has helped push the price of lithium carbonate to a peak of $20,694 per tonne in 2018, up from $5,312 in early 2015. The price then backtracked and was recently trading at around $6,700 per tonne.
Producers have scrambled to raise production, but experts are saying the increase in demand and the increase in mining of lithium is damaging to the environment.
Conventional ore mining of hard rock deposits, predominantly in countries like Australia and China, countries of Bolivia, Argentina and Chile have been criticised for the number of fossil fuels used in the processing of the metal.
How is Lithium Mined
Most lithium is commercially produced from either the extraction of lithium-containing salts from underground brine reservoirs or the mining of lithium-containing rock, such as spodumene. Brine is pumped from beneath the salt flats into vast evaporation pools, a process that leaves behind lithium carbonate.
It requires vast quantities of saltwater and locals in Chille worry about the effect on their water supply.
In regions like Argentina’s Salinas Grandes, local people are resisting further developments by mining firms.
But now technology firms claim they have a possible answer to the issue.
While their methods differ, they broadly fit under the umbrella of direct extraction technologies, which involves filtering the lithium carbonate directly from the brine, rather than relying on solar evaporation.
Research On Environmentally Safe Lithium Mining Technology
For the past six years, Prof Huanting Wang and a group of researchers led by Monash University in Melbourne has been working on a new technology that uses synthetic membranes to filter out the lithium from the brine.
“It can potentially improve productivity and environmental sustainability by reducing chemical use and waste,” he says.
California-based company Lilac Solutions has also developed a direct extraction technique.
David Snydacker founded Lilac in 2016, and this year the company raised $20m (£14.5m) in funding in a round led by Breakthrough Energy Ventures, which is backed by Bill Gates.
Lilac uses an ion exchange technology that absorbs the lithium from the brine, resulting in higher recovery rates than evaporation ponds.
After we’ve recovered the lithium, the only difference with the brine is that the lithium has gone and that brine can be put back underground to maintain the water levels in the reservoir, and to make sure that we’re not impacting nearby freshwater,” Mr Snydacker says.
“For people living in these communities, water scarcity is a very real, tangible issue. If you drive out into these regions it is very, very, dry and you are hundreds of kilometres from the nearest big city,” he adds.
Lilac has partnered with Australian company Lake Resources, who have adopted the technology and are exploring the potential for direct extraction from their flagship Kachi project in Argentina.
These direct extraction technologies can also potentially address the supply issues experienced by producers that contributed to the surge in the lithium price back in 2015.
Direct extraction technologies can extract lithium in hours, rather than the months usually required.
And that supply will be needed – the electric vehicle market is forecast to grow by 29% annually for the next 10 years, requiring more batteries, and more lithium components.
While this is all promising, the future widespread commercial success of these technologies is not a foregone conclusion.
“[There are] still significant challenges to commercialisation. It’s still very early days,” says Andrew Miller from Benchmark Mineral Intelligence.
“The expansion of lithium projects, particularly when you factor in commercialisation of new technology, has a very low success rate in the lithium market. Even major producers typically come in behind schedule and over budget.”
A skills gap may also be exposed within the industry, with lithium expertise stuck in traditional evaporation ponds knowledge rather than the newer technologies. As Mr Snydacker puts it, this “cultural inertia could become difficult”.



