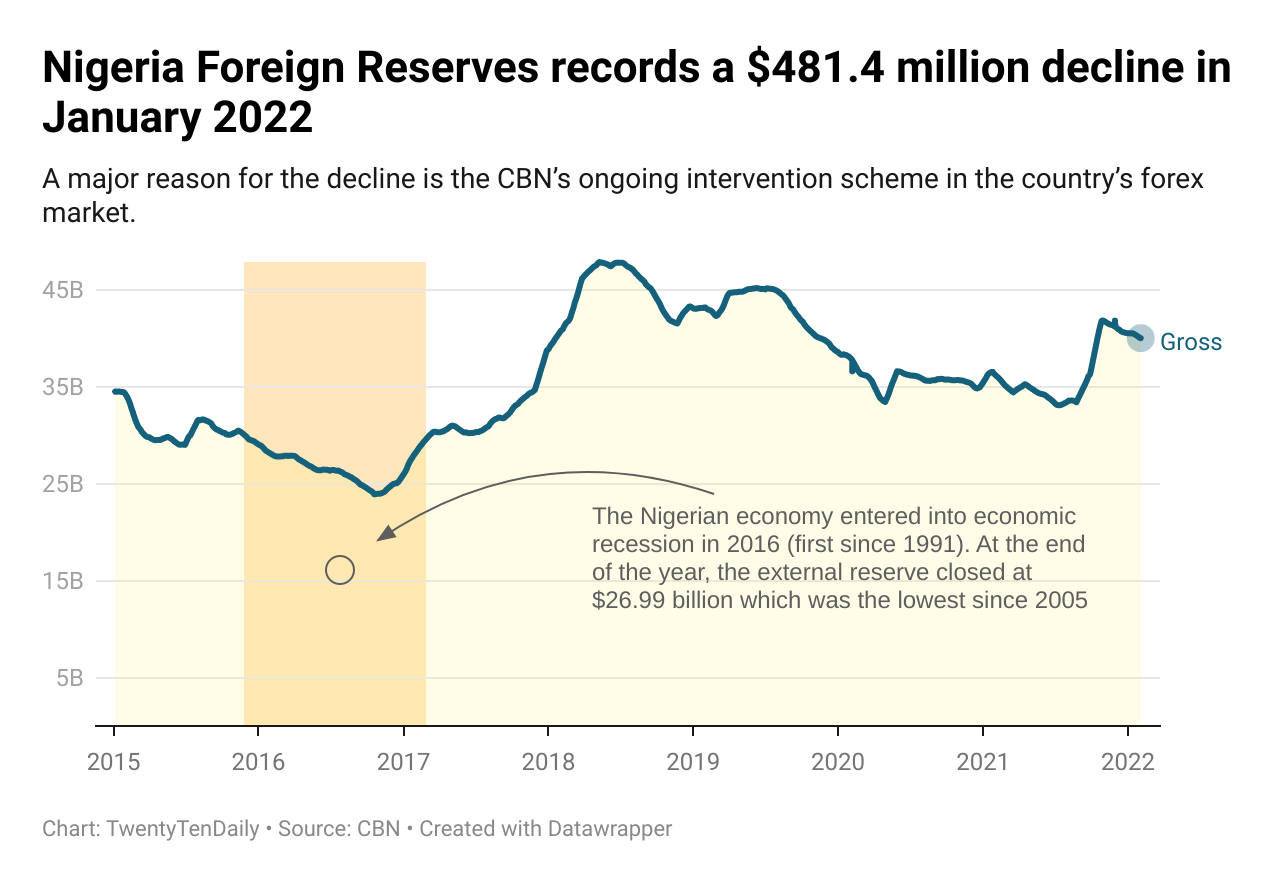
New figures made available by the Central Bank of Nigeria (CBN) has revealed that the West African country’s foreign reserves recorded a $481.4 million decline in January 2022 to close at $40.04 billion, showing a 1.2% fall from the previous month.
Data from the CBN show a steady monthly decline from November 2021 till now. Foreign reserves lost $611.01 million in November 2021, $66.17 million in December and $481.4 million in January 2022.
After dropping to one of its lowest in March 2021 at $34.74 billion, representing a year-to-date decline of $632.9 million (1.79%), Nigeria’s reserve received a $4 billion Eurobond secured by the federal government in September 2021 and an additional $3.35 billion IMF facility, bolstering funds to $5.99 billion in October.
Unfortunately, November’s $611.01 million loss against the previous month’s gains set the stage for the steady decline experienced in the following months.
Reasons for the decline
A major reason for the decline is the CBN’s ongoing intervention scheme in the country’s forex market. The apex bank has continued to supply dollars to help meet forex demands and stabilize the currency market. Data from the CBN statistical bulletin for Q3 2021, shared that the apex bank supplied a sum of $8.97 billion in the forex market through the Importers, Exporters and SME windows.
The bank also supplied $1.42 billion through interbank, while $2.77 billion was channelled through BDC operators between January and June 2021, before the sale of FX was discontinued by the apex bank in 2021.
The crash in crude prices due to the covid-19 pandemic, as well as the downtrend in foreign investments, has also contributed to the decline in Nigeria’s foreign reserve. Nigeria’s inability to meet up with its crude production quota, as well as secure foreign investments allows for the piling pressure on the supply of FX in the country.
For instance, despite oil already trading at a record high of $90 per barrel, Nigeria has been unable to reach its supply target, thereby losing out on its major opportunity to boost FX earnings.
About external reserve
A country’s foreign reserves are assets held on reserve by the central bank to back liabilities and influence monetary policy. They include foreign banknotes, deposits, bonds, treasury bills and other foreign government securities.
These assets serve many purposes but are most importantly held to ensure that the government or its agency has backup funds if the national currency rapidly devalues. Foreign exchange reserves are also called international or external reserves.

