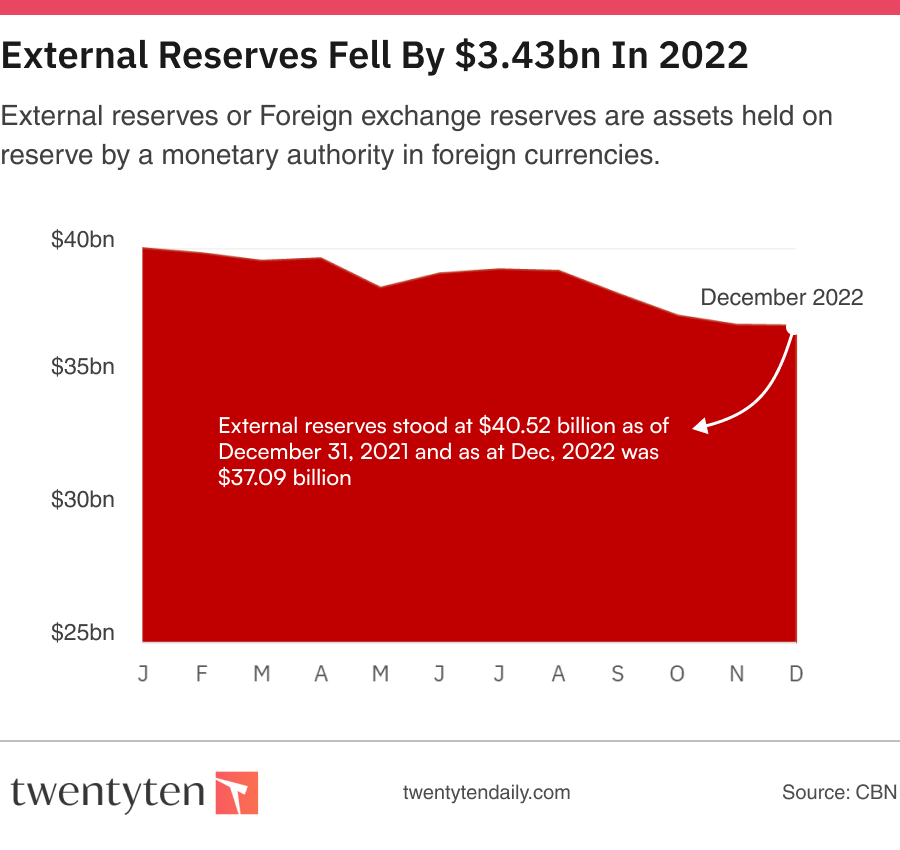
According to figures obtained from the Central Bank of Nigeria, the country’s external reserves fell by $3.43 billion in 2022.
CBN disclosed that the reserves which stood at $40.52 billion as of the end of December 31, 2021, ended December 29, 2022, at $37.09 billion.
External reserves or Foreign exchange reserves are assets held on reserve by a monetary authority in foreign currencies. They are used to back liabilities and influence monetary policy. They include foreign banknotes, deposits, bonds, treasury bills and other foreign government securities.
At the last Monetary Policy Committee meeting of the CBN in November, the CBN Governor, Godwin Emefiele, said, “The committee observed the decline in the external reserves position, as gross external reserves decreased by 1.34 per cent at end-October 2022 to $36.87bn, from $37.39bn at end-September 2022.
“With indications of lower crude oil prices in the futures market, members urged the Bank to sustain its current policies to boost non-oil exports in order to shore up the external reserves.”
A member of the MPC, Robert Asogwa, said, “The recent drop in external reserves is, however, linked to the decline in oil exports even at a time of higher oil prices.
“Interestingly, the publicised reduction in oil thefts across the Niger delta and the rising prospects of increased overseas remittances would likely boost the gross external reserves to a large extent in early 2023.”

