Back in November 2021, a UK based nurse was admitted to Intensive Care after contracting the coronavirus. According to the Sun, 37-year-old Monica Almeida was placed on a ventilator after her condition deteriorated.
However, Almeida recounts that Viagra was administered during treatment which opened up her airways and saved her life. Almeida eventually left the hospital on December 24.
Almeida’s account has left many with the ultimate question, which is, can Viagra be a viable treatment for Covid-19?
Viagra, otherwise known as sildenafil, is familiarly used for treating erectile dysfunction. It also increases blood flow in the body by relaxing muscles cells and thus, blood vessels, causing them to widen (vasodilation).
In 2020, a paper titled: Hypothesis of COVID-19 Therapy with Sildenafil, looked into the potential benefit of using Viagra (Sildenafil) to treat COVID-19. The researchers established that since viagra can effectively treat high blood pressure in the lungs, a condition known as pulmonary hypertension, it can be used to treat both bacterial and viral lung infections that causes widespread inflammation in the lungs. Inflammation of the lungs is one of the varying effects of COVID-19.
As inflammation sets in, it can damage the lung tissue, cause the formation of blood clots and increase the risk of pneumonia. The study proposed that Viagra could potentially counteract some of these effects but wanted funding to investigate this further.
Another research tried to determine if the impacts sildenafil and nitric oxide have on the body can help prevent and fight the virus that causes COVID-19. Nitric oxide is a gas that acts as a signalling molecule and messenger. One of the biological processes nitric oxide induces is preventing blood clotting and the stimulation of digestive chemicals, including being used by the inner lining of blood vessels to signal muscles to relax.
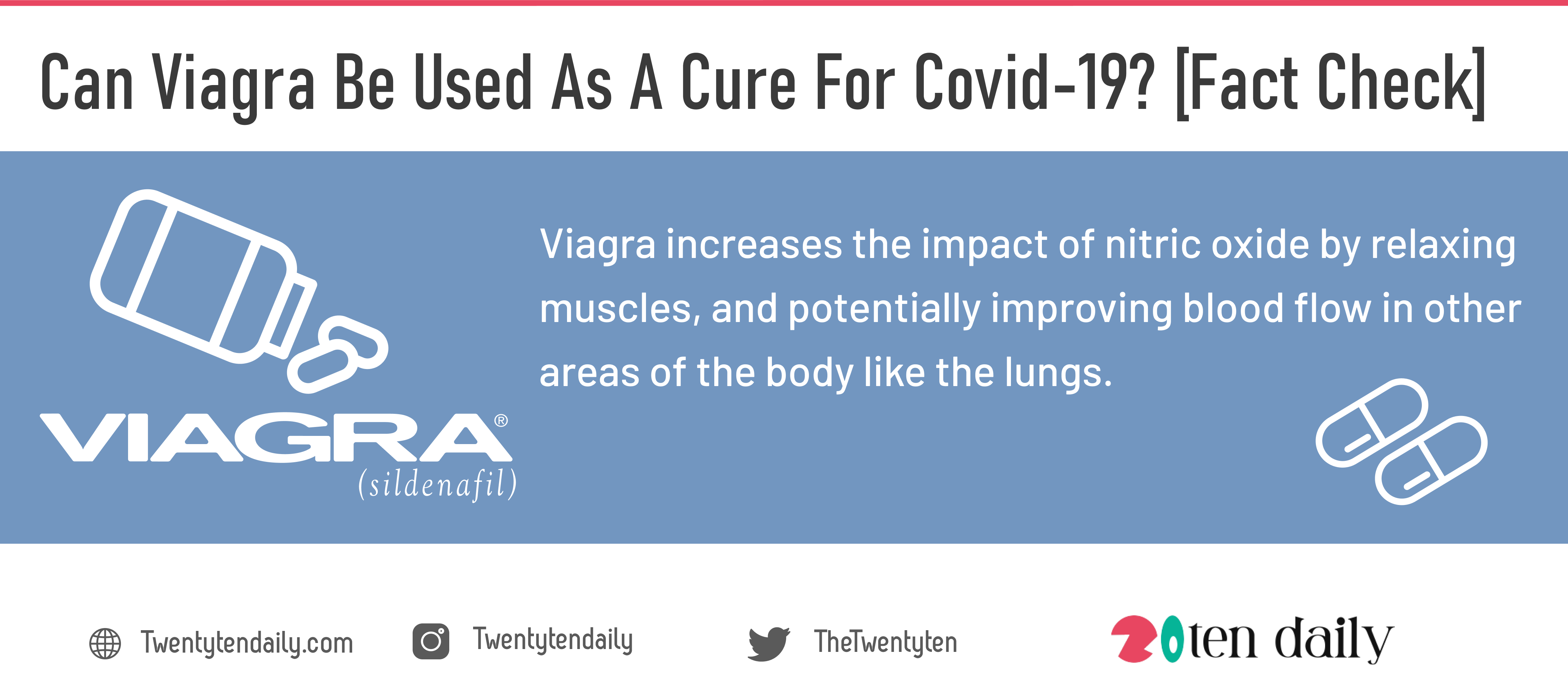
When used together, viagra increases the impact of nitric oxide by relaxing muscles, and potentially improving blood flow in other areas of the body like the lungs. This means that nitric oxide can potentially impact blood vessels by opening them and potentially aiding in oxygen circulation in the lungs, potentially helping patients with respiratory challenges.
Others studying the gas hope that it can improve blood oxygen levels, prevent viral replication and even help shorten the amount of time COVID-19 patients require ventilation. The study is yet to be concluded.
One small-scale study showed that sildenafil treatment could have a “potential therapeutic role” for patients but that a large-scale study would be needed to confirm these results.
Conclusion
Varying research all favour the sildenafil group compared to the placebo group in treating lung-related infections in Covid-19 patients but researchers have stressed that for now, it was not possible to conclude that the favourable differences were attributable to sildenafil. Trials would continue till a pair peered conclusion is reached.
Other Drugs Recommended For Covid-19 Treatment
The World Health Organization has recommended two new drugs for COVID-19, providing more options in the treatment of the virus. The paper published on January 14, 2022, revealed Baricitinib, which is strongly recommended for patients with severe or critical COVID-19 and Sotrovimab which is an alternative to casirivimab-imdevimab, a monoclonal antibody cocktail recommended by WHO in September 2021.
Baricitinib is an oral drug, used in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. It works by suppressing the overstimulation of the immune system if used alongside corticosteroids. For sotrovimab, studies are ongoing on the effectiveness of monoclonal antibodies against Omicron but early laboratory studies show that sotrovimab retains its activity. This means it could potentially protect patients from the Omicron variant.
Evidence from seven trials involving over 4,000 patients with non-severe, severe, and critical COVID-19, showed the same results.
Experts have also looked at two other drugs for severe and critical COVID-19 which are ruxolitinib and tofacitinib.